What is DEXA Bone Densitometry and how does it work?
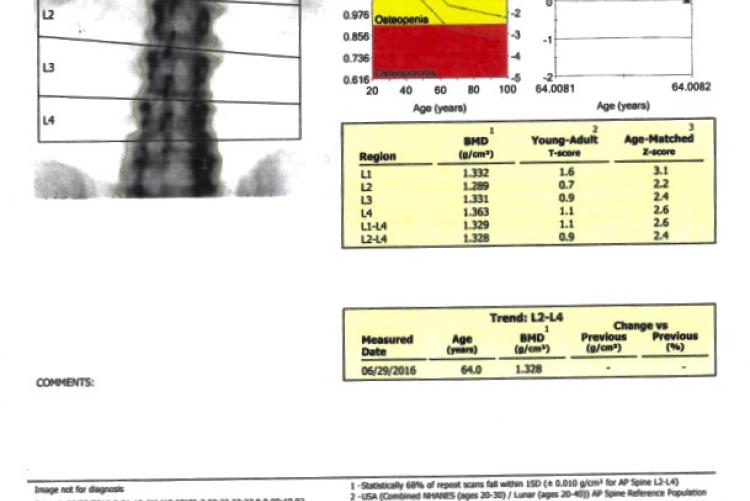
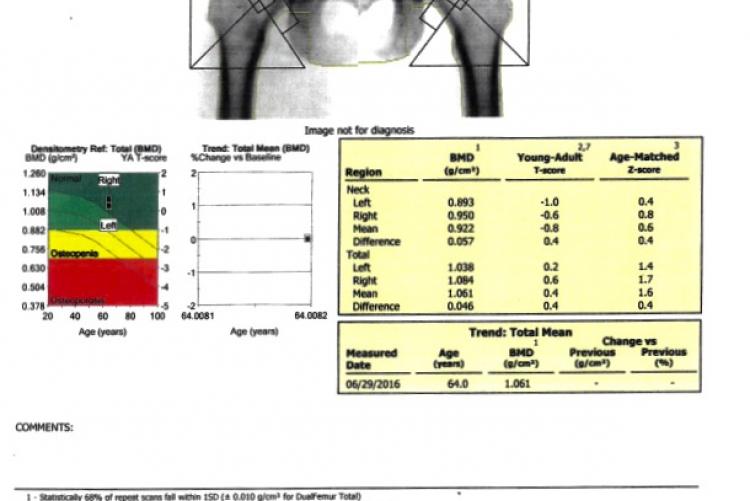
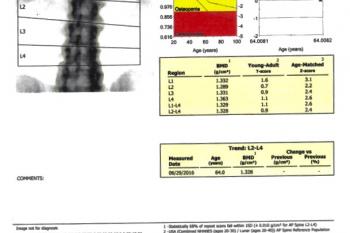
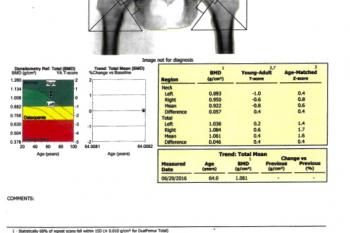
DEXA stands for “Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry.” It is the most widely used technique for measuring bone mineral density (BMD) and diagnosing the presence of osteoporosis. X-ray beams of two differing energies are passed through the spine and hips, and a computer analyzes the difference in absorption of the X-rays to determine the BMD. We examine spine and hips because these are the areas that osteoporosis affects first. The DEXA test result is reported as a “T-score” – which compares a patient’s bone mineral density to that of a healthy young person.
“I scheduled my digital mammogram and bone densitometry exam on the same day. I was glad I didn't have to come back another day and take more time off work.”
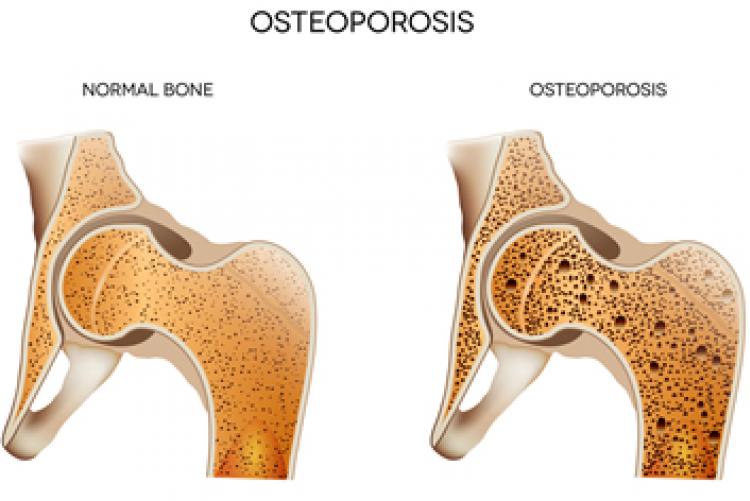
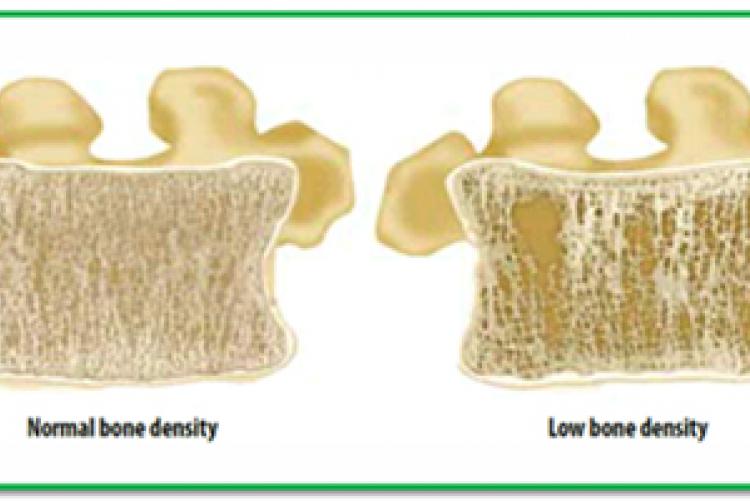
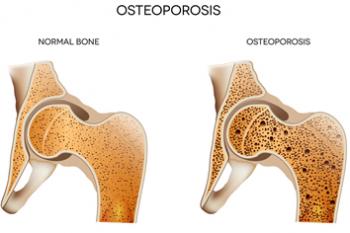
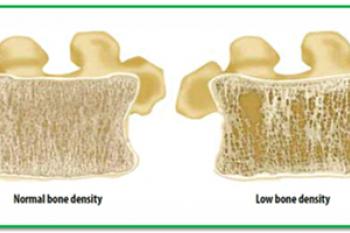
What is Osteoporosis?
The World Health Organization defines Osteoporosis as abnormally low bone mineral density (BMD), with a T-score of –2.5 or less. This means that bone mineral density has dropped so much that the chance of a fracture, even with minimal trauma, is significantly increased. It is common to gradually lose bone strength after the age of 30, so osteoporosis is unfortunately very common in older individuals, especially women.
Risk factors for osteoporosis:
- Family history of osteoporosis or fractures caused by osteoporosis, such as hip fractures, wrist fractures, loss of height, dowager’s hump
- Being of Caucasian or Asian descent
- Slender, thin frame, small-boned
- Post Menopausal or early menopause
- Sedentary lifestyle—lack of regular exercise
- Low calcium in the diet
- Alcohol or tobacco use
- Eating disorders, including anorexia nervosa and bulimia
- Long term use of certain drugs, such as steroids and anticonvulsants
“Everyone I met at River Radiology was kind and helpful, from the person who scheduled my appointment, to the receptionist and technologists. This is the best medical office I have ever been to.”
Why is early detection of Osteoporosis so important?
There are now several medications that can effectively treat osteoporosis and reduce the chance of a debilitating fracture. The likelihood of osteoporosis occurring in the future can be predicted by noting the presence of a lower-than-average bone mineral density, a condition called “Osteopenia”. By beginning early treatment, osteoporosis can usually be prevented.
Your DEXA bone densitometry examination
Do not take any calcium or calcium product, such as Tums, for 24 hours prior to the exam. Dress metal-free (without zippers) from the waist down. The exam takes about 15 minutes, but you should expect to be here for about 30 minutes in total. You will be asked to lie still on a comfortable table while low-dose X-rays are used to analyze the mineral content of both your spine and hip bones. The amount of X-ray used is extremely small – equivalent to about 1/10 the dose received from a chest X-ray.
What is Vertebral Assessment?
Vertebral Assessment, called VA, is performed using state-of-the-art bone density equipment now available at River Radiology. VA allows the simultaneous diagnosis of existing vertebral fractures and bone mineral density in a single, brief exam session. The procedure exposes the patient to only about 1/100th of the radiation dose of a conventional x-ray. The analyzed report of the combined bone density and VA test results better help identify patients at risk for osteoporosis and more accurately determine their individual fracture risk.
When can my physician expect a copy of my report?
In most cases, reports are provided within two business days.
For more information about osteoporosis and bone densitometry, speak to your physician or contact the National Osteoporosis Foundation, 1150 17th St. N.W., suite 500, Washington D.C. 20036-4603 (phone: 202-223-2226; website: www.nof.org). You can get additional information as well as treatment options by visiting the National Council for Aging Care http://www.aging.com/osteoporosis-defined-causes-symptoms-and-treatment/